The future of abundant solar power in space starts now. We are excited to be leading Solestial’s seed round, and look forward to supporting the team as they bring low-cost, lightweight solar power to space. Here are several building block questions that led to our investing in the company:
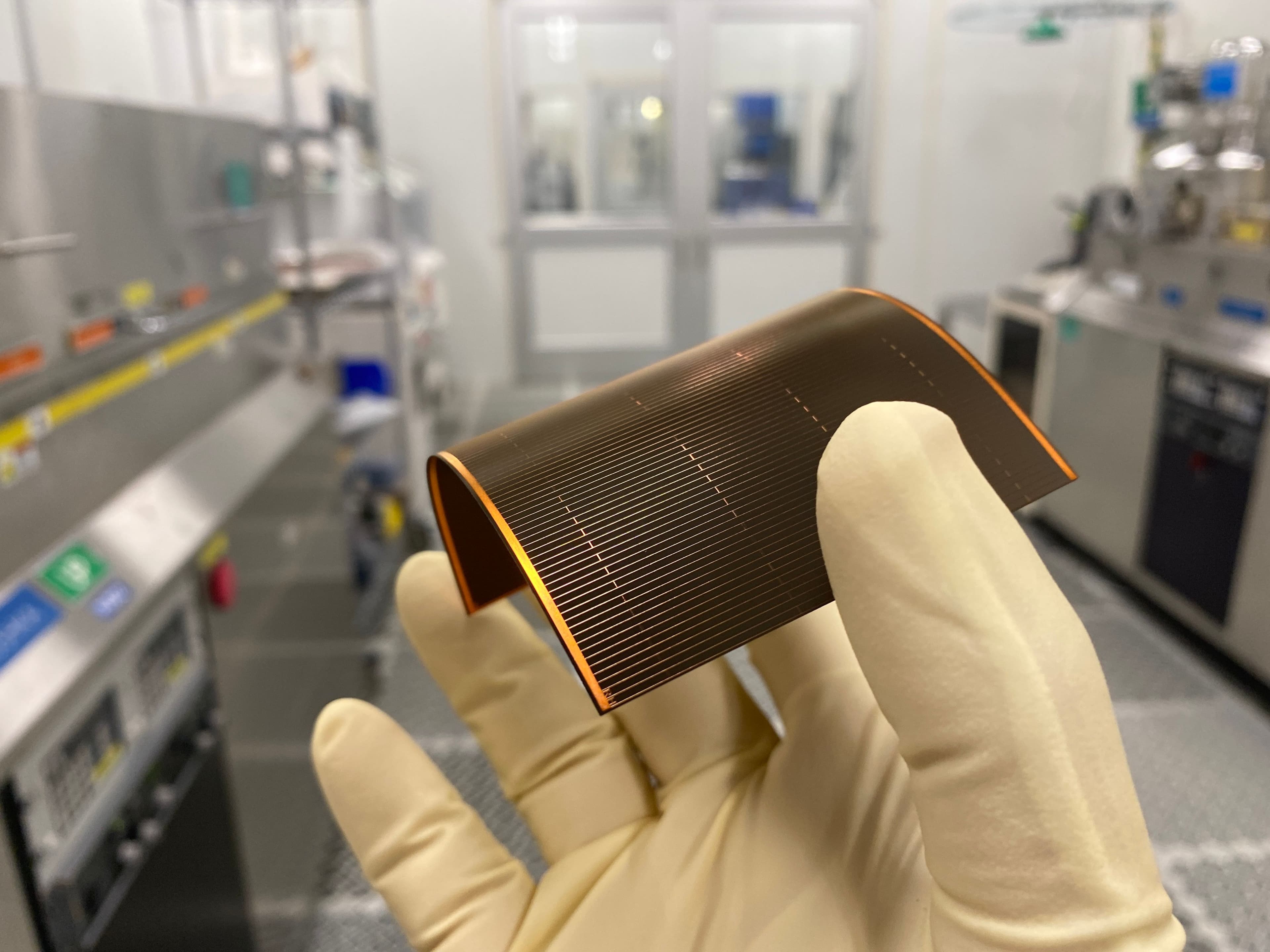
What is Solestial trying to do? Solestial is leveraging a decade of innovation in materials science and photovoltaics coming out of Arizona State University to bring low-cost, lightweight silicon solar cells to the space industry. These thin and flexible cells will have greater than 20% end-of-life efficiency and can cure themselves from radiation damage at normal operating temperatures. What are the industry opportunities? Solar power for in-space applications is expensive, and manufacturing processes are not able to scale to meet demand in the coming years. Low-cost silicon solar panels used in terrestrial applications degrade rapidly when subjected to the extreme temperature cycles and particle radiation experienced in orbital environments. These are not suitable for missions lasting more than a couple years. How is it done today? Most solar cells for in-space applications are made from expensive materials (like gallium arsenide) and involve challenging manufacturing processes that do not scale. The cells alone cost hundreds of dollars per watt, and satellite manufacturers procure the cells from one provider and the deployable structures from another. They then mechanically and electrically connect the cells to the panels before integrating and testing with the rest of the satellite. Overall, the time and materials involved in the solar power system for satellites can account for 30% of the cost of the entire satellite. Why do we think Solestial will be successful? Using silicon as their base material, Solestial can utilize well-established silicon manufacturing processes to ensure production capabilities can scale with demand. Eventually, they will look to automate the manufacturing of the entire solar array system – further reducing costs for satellite manufacturers and improving performance. Combining inexpensive materials with well-known manufacturing processes (and a few proprietary changes) allows Solestial to offer efficient solar power for space assets at a 10x lower price-point. When they are successful, what difference will it make? Cost to access space has decreased dramatically in the last 2 decades due primarily to new launch services and the microelectronics revolution. However, there are still legacy technologies, like solar cells, that have not progressed in the same manner. Once in space, everything revolves around power, and expensive solar panels are a major barrier in the way of power abundance. Solestial’s low-cost, lightweight cells can catalyze many elements of the orbital and cis-lunar environments including in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing (ISAM). Additionally, the “holy grail” of near-Earth orbit applications is beaming power down from space so that terrestrial solar cells can provide reliable energy throughout the night. The US, China, and ESA, have all announced power-beaming demonstration missions in the coming decade. Power beaming, ISAM, and other energy-intensive in-space applications will need massive arrays of low-cost, lightweight panels in orbit, and we believe Solestial has the team and technology to meet this demand. Photo Source: SolestialBy Mat Costes and Taylor Sargent